Convex and Affine Set
Line in Euclidean Space
A line through two points
is defined as A line segment between two points is defined as
Affine Set
An affine set contains the line through any two distinct points in the set:
e.g. An entire 2D plane.
Theorem
Every affine set can be expressed as the solution set of a system of linear equations.
Convex Set
Let
be a vector space. A subset of is convex if whenever and , we have � . That is it contains the line segment between any two distinct points in the set:
e.g. 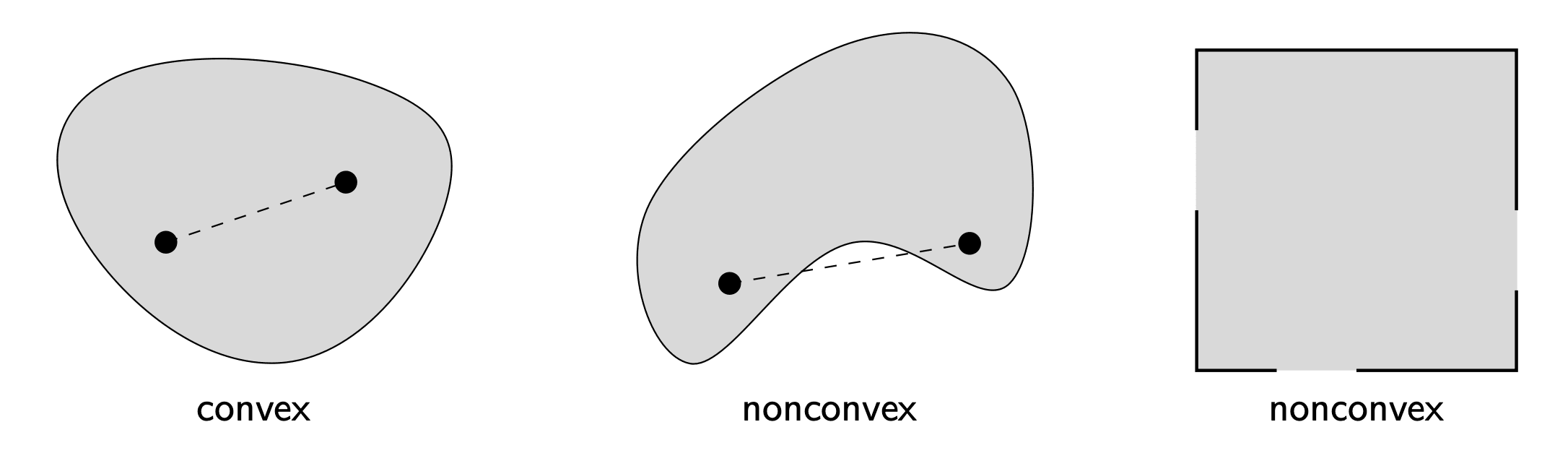
Convex Combination
A convex combination of
is any point of the form: with and .
Convex Hull
The convex hull of a set of points
, denoted , is the set of all convex combinations of the points in .
Proposition
The convex hull is the smallest convex set to contain all the points in the set
.
Cones
Convex Cone
Conic Combination
A conic combination of points
and is any point of the form: with and .
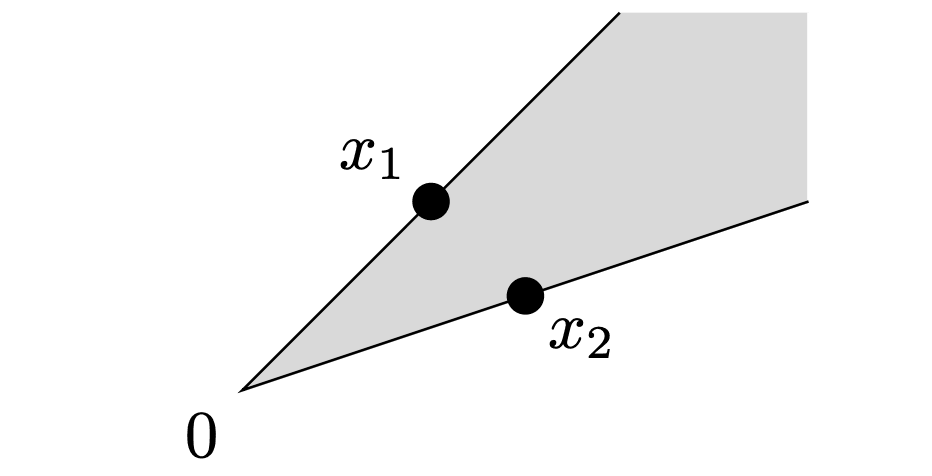
Cone
A cone is a set
containing all non-negative multiples of its points:
Convex Cone
A convex cone is a set containing all conic combinations of its points.
Proper Cone
e.g.
- Nonnegative orthant
is a proper cone. - Positive semidefinite matrices
is a proper cone. - Second-order cone
is proper.
Dual Cone
The dual cone of a cone
is
Positive Semidefinite Cone
Real Symmetric Matrices
We have the following notation for real symmetric matrices:
is the set of symmetric matrices : positive semidefinite matrices: : positive definite matrices
Proposition
Prop
iff all eigenvalues are real and nonnegative.
Proposition
Prop
is a convex cone.
Hyperplanes, Halfspaces and Polyhedron
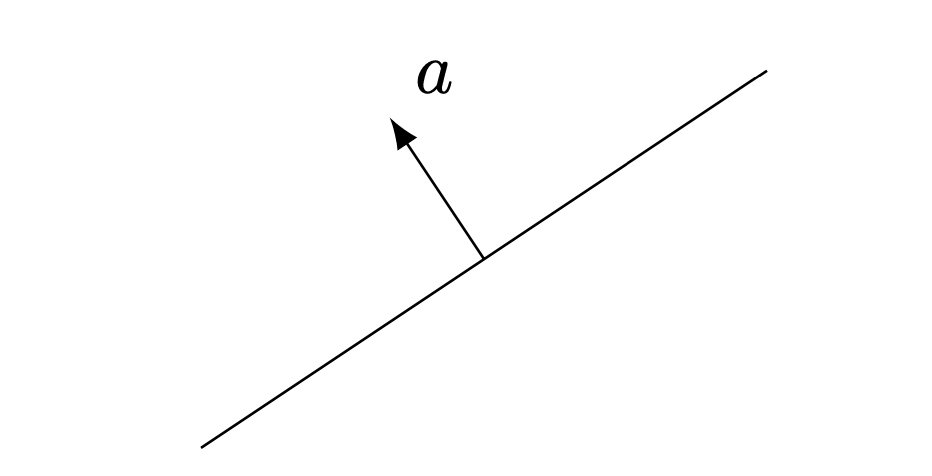
Hyperplane
A hyperplane is a set of the form
with . And we call the normal vector.
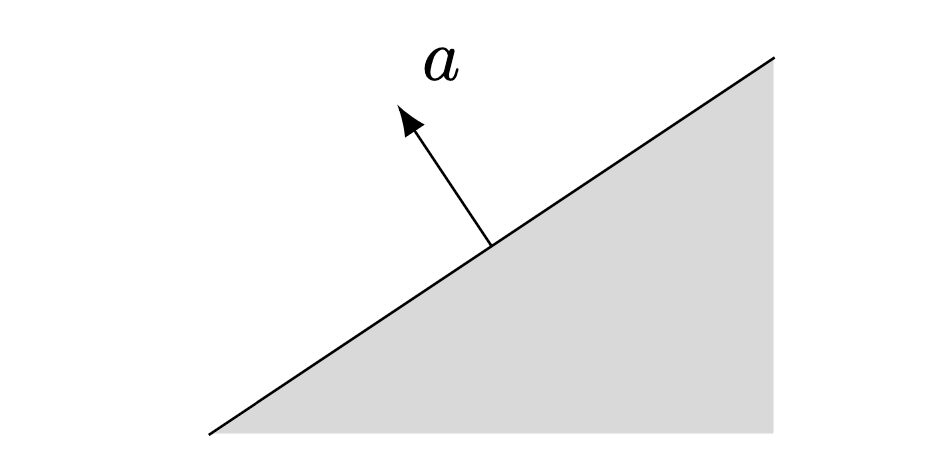
Halfspace
Halfspace is a set of the form
with .
Prop Convexity of Hyperplane and Halfspace Hyperplanes are affine and convex, while halfspaces are convex.
Polyhedron
A polyhedron is the intersection of a finite number of halfspaces and hyperplanes.
Proposition
A polyhedron is the solution set of finitely many linear inequalities and equalities:
where , , is component-wise inequality.
Polytope
A polytope is a bounded polyhedron, i.e. a polyhedron with a finite number of extreme points. Equivalently, it is the convex hull of a finite number of points.
Balls and Norm
Euclidean Balls and Ellipsoids
Def Euclidean Ball
A (Euclidean) ball with centre
Def Ellipsoid An ellipsoid is a set of the form:
where
Norm Balls and Norm Cones
Def Norm Cone
A norm ball with centre
Prop Norm balls and norm cones are convex.
Summary of Common Convex Sets
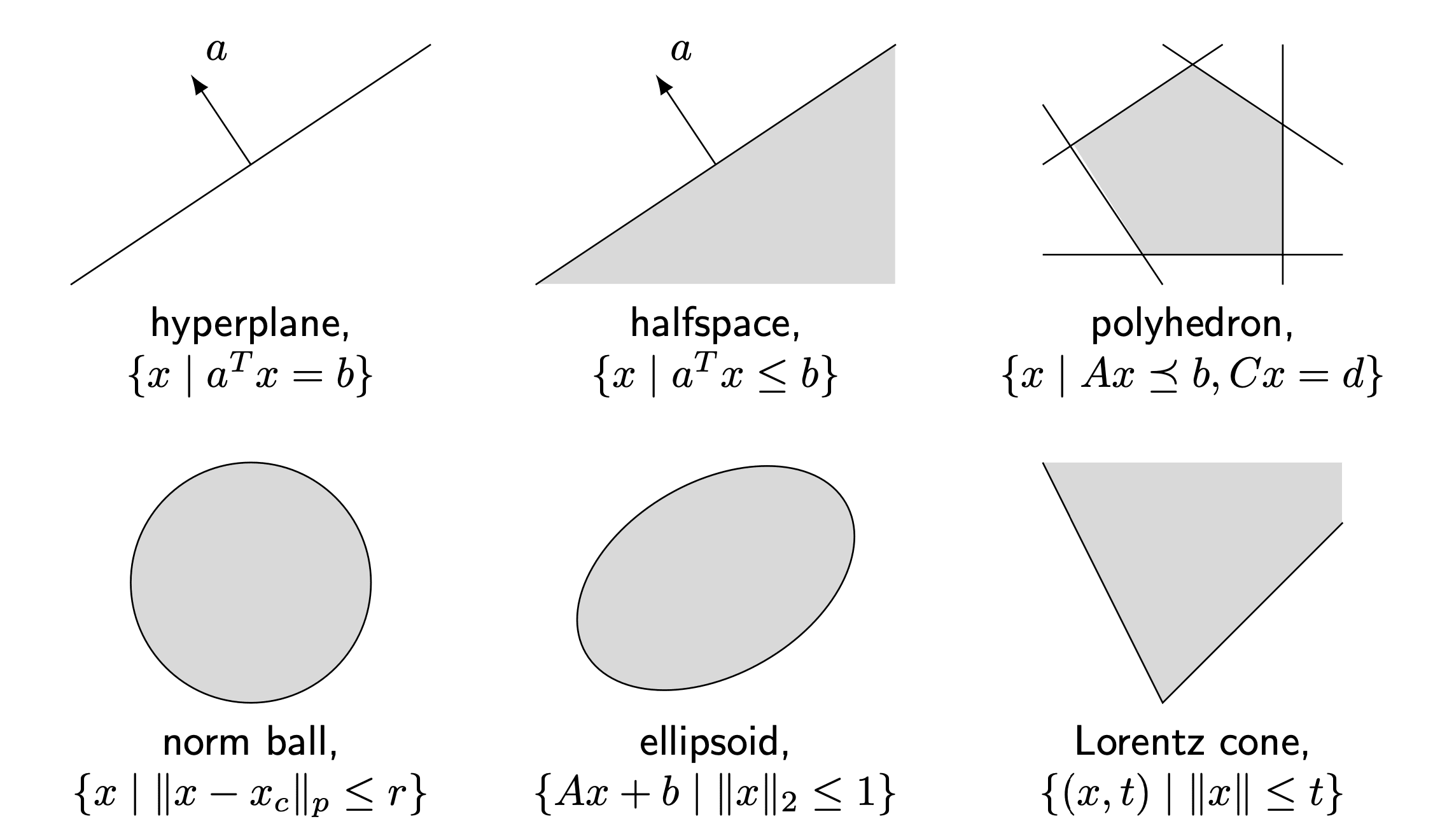
Operations that Preserve Convexity
Proposition
The intersection of arbitrarily many convex sets is convex.
Def Affine Function
A function
Prop The image of a convex set under affine function
Proposition
The inverse image
of a convex set under affine function is convex:
Perspective Function
A perspective function
is defined as:
Prop Images and inverse images of convex sets under perspective are convex.
Def Linear-Fractional Function
A linear-fractional function is defined as:
Prop Images and inverse images of convex sets under linear-fractional functions are convex.
Generalized Inequalities
Generalized Inequality
A generalized inequality relation defined by a proper cone
satisfies where denotes the interior of .
Prop
Prop
Minimum
is the minimum element of with respect to if
Minimal
is a minimal element of with respect to if (for any)
e.g. Here 
Proposition
Minimum if exists, must be unique; however, several minimals may be found for
given an generalized inequality induced by a proper cone .
Separating Hyperplane Theorem
If
and are nonempty disjoint convex sets, there exists and such that That is the hyperplane separates and .
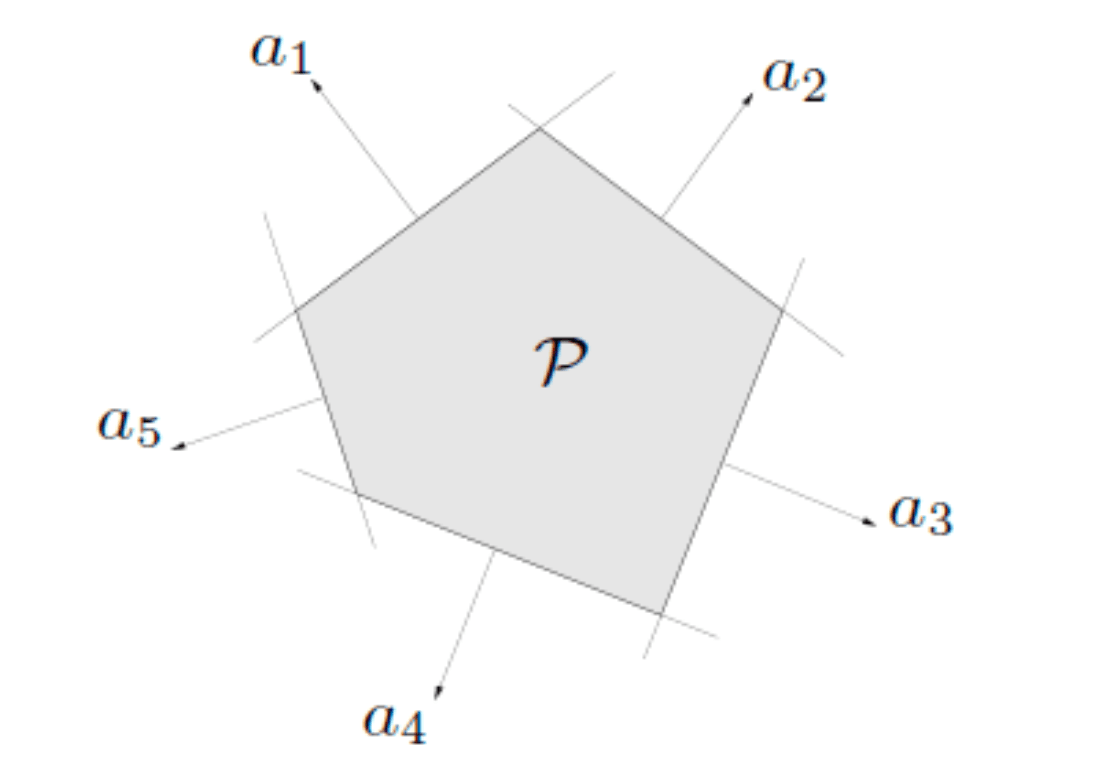
Supporting Hyperplane Theorem
A supporting hyperplane to set
at boundary point is where and for all . And if is convex, then there exists a supporting hyperplane at every boundary point of .